WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 Troubleshootingwifi.Com are the 2 choices that most people use. Lot of product promotions or technical news may tell you that WiFi 5 and WiFi 6 are different generations of WiFi, with WiFi 6 being newer with higher performance.
If you’re considering getting the most recent generation, you need to think about your options. To make a rational choice, you have to perceive the key variations between WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6.
What’s WiFi 5?
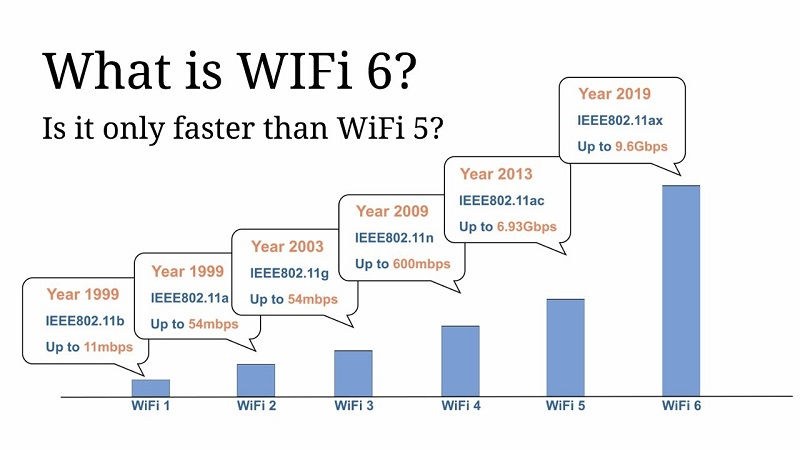
WiFi 5 is the fifth generation of wireless networking standards in the IEEE 802.11 that provides high outturn in a wireless local area network (LAN) using the 5GHz band frequency. WiFi 5 was found in 2014 with many upgrades from the WiFi 4.
Whereas a beautiful innovation, WiFi 5 has its pros and cons. Wi-Fi 5 is the fifth generation of Wi-Fi, preceding Wi-Fi 6. It is an update to the 802.11a standard reigned supreme throughout the 2010s.
Before 802.11ac was dubbed Wi-Fi 5, the quality was known as Gigabit Wi-Fi, because it was the primary Wi-Fi standard to exceed one Gbps. Wi-Fi 5 adopted many capabilities, together with orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing and the ability to work on a 5 gigacycle per second.
Wi-Fi 5 remodeled these capabilities that might benefit and support network technology at the time, including video streaming capabilities and file backups.

What’s WiFi 6?
Wi-Fi 6 is the latest generation of Wi-Fi and aims to enhance the network efficiency. It guarantees an intensive shift in the networking industry, with innovative options that distinct from previous generations.
Wireless fidelity 6 is the official name for the wireless network in the 802.11ax standard. It’s also known as AX WiFi as the successor of 802.11ac. WiFi 6 is an improvement to the WiFi technology in general.
Its principal style is to enhance WiFi in extremely dense environments like malls, residential areas, offices, buildings, etcetera. Found in 2019, IEEE 802.11ax uses 2.4Ghz and 5GHz bands, with the 6GHz band to be introduced.
WiFi 6 is turning into the staple in wireless networking and can be central infrastructure over few years. It’s important to know the WiFi 6 because it has sturdy networking landscape. As IoT becomes the norm, its functionalities are going to be more crucial.
In the close future, more devices may use WiFi 6 with Apple iPhone and Samsung Galaxy Notes already support WiFi 6. The new technology offers connectivity enhancements whereas maintaining compatibility for older devices.
It works better in dense environments, improves the battery lifetime, and boasts more transfer rates than its predecessors.
WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6
WiFi may be a rife technical structure used everywhere the world. Each smartphone has some style of wireless connectivity. WiFi refers to “wireless fidelity” and it’s a technology that uses radio waves to modify computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices to access the internet or communicate with one another through a wireless network.
Since its advent, WiFi has unbroken evolving with a lot of refined standards over the years. Some years back, WiFi 5 was the best wireless standard available. However, WiFi 6 has begun to penetrate the worldwide.
The most recent WiFi standard is compatible with the previous standards. WiFi 6 supports all features of WiFi 5 whereas having more benefits.
• Quicker Speeds
Every generation of WiFi will increase, especially with WiFi 6, although this is not its primary goal. The rates are raised up to 9.6 Gbps, around 40% more of WiFi 5.
• Higher Efficiency
The performance in jammed networks is the ultimate WiFi 6′ signature. It’s referred as “High-Efficiency WiFi” that shines brightest in dense environments like offices, malls, and apartments.
Whereas the nominal rate improvement is around 40%, the improvement over a whole network is 300%. This interprets to 75% lower latency. WiFi 6 maintains steady high speeds while connected to several devices simultaneously.
• Improved Battery Life
Target Wake Time (TWT) reduces their life to send or receive data. This feature will increase device sleep time and improves battery life.
• For IoT Devices
IoT is, simply, any device that connects to the internet. It has low latency, low speed, and low power consumption. With the increasing of IoT devices each day, the internet needs to be structured. WiFi 6 has low-power enhancements that are well-suited for IoT devices.
TWT permits for access points to speak to connected devices to wake or to sleep. It allows the devices to conserve power, leading to longer battery life, permitting more IoT devices in the home to use the internet.
• AP Capacity
The Wi-Fi 6 most innovative feature is OFDMA. It’s an upgrade of Wi-Fi 5 OFDM that encodes multiple frequencies to scale back the interferences.
OFDMA enhances these capabilities and permits Wi-Fi 6 APs to attach to multiple purchasers, whereas Wi-Fi 5 APs hook up with one channel. OFDMA is multiuser support, that creates Wi-Fi 6 more economical, less request response times.
• AP Spatial Streams
WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 are different in spatial streams, that are multiple signals that antennas transmit in a single channel at MIMO environments. Wi-Fi 5 APs supply four spatial streams, with the potential to eight spatial streams.
Wi-Fi 6 APs have eight spatial streams, which is more accomplishable in the latest generation of Wi-Fi. With more streams, Wi-Fi 6 gains higher speeds, which suggests to perform quicker.
#WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 – • Frequency Band
Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 5 frequency bands differ which affects to the outturn. Wi-Fi 5 uses the 5 gigacycle per second frequency band for the transmission, whereas Wi-Fi 6 can use each the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
• Maximum Data Rate
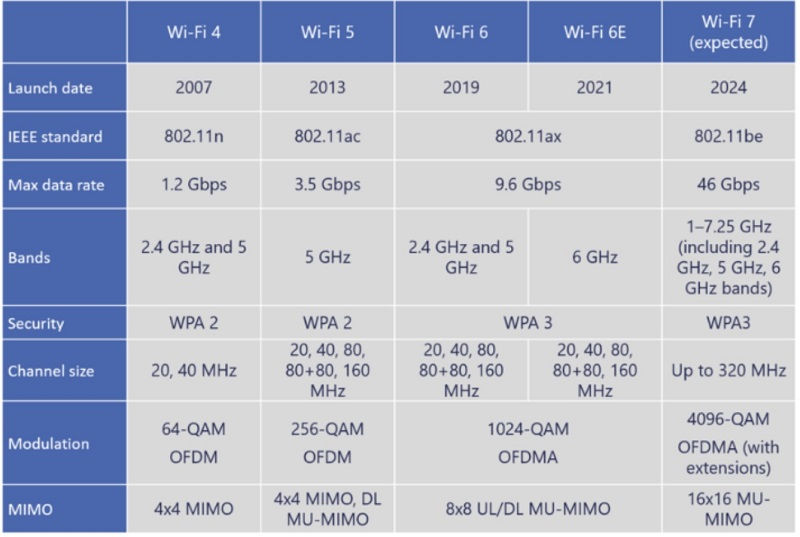
AP capacity, spatial stream and frequency are influencing the most rates for Wi-Fi 6. Whereas Wi-Fi 5 rate was around 6.9 Gbps, it might reach below the ideal circumstances. The speed for Wi-Fi 6 is 9.6 Gbps with the secure advancements and new features.
• MU-MIMO
Old MIMO permits data sources and destinations to communicate through multiple antennas. MU-MIMO will do this, nevertheless it will support multiple users at one network setting at constant time.
Wi-Fi 5 uses downlink MU-MIMO, whereas Wi-Fi 6 supports biface MU-MIMO for each transmission and downlink capabilities. Wi-Fi 6 will modify multiple users to transfer simultaneously, and Wi-Fi 5 can’t. Wi-Fi 6 MU-MIMO guarantees for increased speed.
#4. Reasons You Must Upgrade To A WiFi 6
If you’re full of buffering, your router isn’t the reason! Just get the super-fast WiFi 6 technology. Designed to extend the network capability and the performance, WiFi 6 (802.11ax) is the latest generation of WiFi technology.
It’ll give you with quicker WiFi speeds and reliable connections, therefore you’ll be buffer-free, faster downloads, and enhance your web experience. Engineered to deliver the quickest WiFi for nowadays, here are why your next router must be a WiFi 6.
• Provides The Best Performance
The most recent WiFi 6 has better performance compared to WiFi 5 (802.11ac) technology. Whereas WiFi 5 brought gigabit speeds, it falls short on delivering connection because more devices on the network.
WiFi 6 uses orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA), a feature that will increase overall network efficiency to permit many devices to attach to your WiFi.
• Provides The Quickest Speeds
Every band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) is formed of part streams. WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 carry the best number of streams. WiFi 6 will increase the quantity of streams across the 2.4 and 5 gigacycle per second bands, whereas WiFi 5 has a limit of eight in a twin band configuration.
This increase of streams speed and your devices have more methods to communicate with your WiFi router. In fact, WiFi 6 enabled client devices relish a 40% increase in speed.
#WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 – • It’s Intended For Smart Home
IOT applications are proliferating. As a result, connected devices in the home are growing. WiFi-connected lightbulb, smart switch, door lock, or camera may connect your WiFi network.
WiFi 6 has been designed to handle many devices without impacting the speeds. This ends up in a swish streaming experience, without interrupting lights, switches, thermostats and other IOT devices.
• Ideal For 4K/8K UHD Streaming
Streaming 4K or 8K video needs a high-speed connection. With multiple users, streaming high-definition video puts a bigger load on the network.
With a mixture of ultra-fast processors, enhanced memory and the increased range streams, WiFi 6 is best for streaming multiple high definition video without buffering or annoying.

#WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 – So, Should You Upgrade Now?
The short answer is probably “yes”. Devices that support Wi-Fi 6 are getting more common, together with each higher-end models. Most devices are operating on 802.11ac, it’ still well worth to think about a Wi-Fi 6 upgrade.
Costs are coming down on both standalone Wi-Fi 6 routers as well as wireless mesh systems that give wall-to-wall coverage. Meanwhile, adding a Wi-Fi 6 extender may be an alternate if you’re pleased with your existing Wi-Fi 6 router for a bigger home or in a dense neighborhood with countless wireless signals.
Wi-Fi 6 aims to alleviate network congestion, give bigger capability, and scale back the power consumption. Wi-Fi 6 uses OFDMA modulation, that allows up to thirty clients to share a channel at constant time, boosting the overall capacity whereas reducing latency.
OFDMA permits them to get more accessible network channels. If one person in your house is streaming and another is checking social media, OFDMA permits a router to assign channels to every device.
Wi-Fi 6 uses Target Wake Time (TWT) that extends the battery lifetime like smartphones and tablets, similarly with security cameras and video doorbells. The new customary takes advantage of unused radio frequencies to produce quicker 2.4GHz performance, and it uses refined management to increase Quality of Service (QoS) options.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 offers more transmission with Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO), that streams data at the same time instead of sequentially, permitting for sharing of information among connected MU-MIMO clients.

Read Also:
WiFi Connected but No Internet: The Problems and Its Solutions
WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 Speed
Wi-Fi 6 is capable of 9.6 Gbps across multiple channels, compared to 3.5 Gbps on Wi-Fi 5. In theory, a WiFi 6 router may hit speeds over 250% faster than WiFi 5 devices due to technology OFDMA, MU-MIMO, and beamforming, that permits higher communication rates.
It has 1024 QAM, which will increase throughput for intensive uses by encrypting more information in the same spectrum. Another addition is WiFi 6E. This works with similar manner that your router reception will broadcast over the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands.
WiFi 6E devices have a new band with a full new set of WiFi channels to cut back network congestion: nearly quadruples the quantity of bandwidth that’s obtainable for WiFi. To place this into perspective, the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands operate at intervals concerning 400MHz.

Can My Device Support WiFi 6?
Currently, some devices are on the market with WiFi 6 compatibility. These devices support the new standard, however they work on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz spectrum.
First, it’ necessary to notice that having a WiFi 6 router doesn’t deliver noticeable improvements. It’s concerning the ecosystem. WiFi 6 guarantees huge benefits in the case of high network utilization. The typical connected devices are predicted to increase, and device makers are working with WiFi 6.
With WiFi 6, the capabilities of MU-MIMO technology are expanding. MU-MIMO, or Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output technology, permits multiple users to access a wireless network at constant time without interruption.
MU-MIMO allows more downlink information to be transferred at once, enabling access points handle more devices at once. WiFi 6 devices will work faster, longer, and have a bigger radius of internet coverage. Getting live-streaming high-quality videos is simply as connecting to the web.

#WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 – WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 Differences
Maintaining with the dynamical WiFi will be challenging, especially for modifications, specifications, and multiplied usability. So, you need to understand the key difference between WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6.
• Power Consumption And Battery Life
The battery life is the most essential specifications people look when considering a new device. Though the ability is consistent enough, it’s neither convenient nor esthetically pleasing. Some devices, in the case of IoT device, don’t seem to be created for perennial charging.
This suggests that a normal WiFi will scale back the quantity of power drained as WiFi tends to strain battery reserves. WiFi 6 offers this battery conservation because of a new feature referred as the Target Wake Time (TWT).
TWT may be a technology that enables unproductive time a computer peripheral spends connected to the WiFi network to be cut down. TWT allows the access point to communicate with a device, instructing it to sleep once not in transmission.
Devices will verify when their WiFi are active to send and receive data, so increasing their sleep time. Whereas this feature might not be convenient for active smartphone users, it’s excellent for IoT setups that don’t need an active internet.
WiFi 5 five doesn’t have the TWT feature and can’t regulate the power consumption by peripheral devices. Thus power consumption is higher.
• Network Security Protocols
The importance of network security will never be over-emphasized. WiFi permits multiple devices and users to be connected by one access point. It is utilized in public places where there’s less management over who can hook up in a network.
Necessary data have to be protected against malicious hackers. WiFi 5 supports the WPA and WPA2 protocols for a secure connection which is important improvements, however it’s vulnerable and weak.
One such vulnerability is lexicon attacks that cybercriminals will use to predict your encrypted parole using multiple combinations. WiFi 6 has stepped up by incorporating the most recent security protocol, WPA3. In short, WLAN 6 used WPA, WPA2, and WPA3 protocols together.
WiFi 6 Protected Access improves multi authentication and coding processes. It’s the OWE technology that prevent car encryption and codes that attach to devices directly.
• Speed Of Data Transfer
Speed is important and exciting feature on new technology. Quicker rates mean shorter transfer times, higher streaming, faster transfer, better video, faster browsing, and so on.
WiFi 5 has data transfer speed of 6.9 Gbps. In real experience, the 802.11ac normal has a data speed of 200Mbps. The speed relies on the Quadrature amplitude modulation and the range of devices connected to router.
WiFi 5 MU-MIMO technology permits four devices to attach simultaneously in lesser speed. WLAN 6 may be a better in terms of speed. It uses 1024 QAM modulation and boasts up to 9.6Gbps.
The distinction between WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 speeds per device isn’t vast. WiFi 6 is faster, however the speed advantage comes when multiple devices are connected to the network. The precise range of connected devices will hardly be noticeable.
• The Beamforming
Beamforming may be a transmission technique towards a selected receiver instead of spreading the signal from different directions. Using beamforming, an access point will send information rather than broadcasting to every direction.
Beamforming isn’t a brand new technology. In WiFi 5, simply four antennas were used. However, WiFi 6 using of eight antennas. The higher the power of the router, the better the rate of the signal.
• OFDMA
WiFi 5 uses Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for network access. It’s a technology that controls the amount of users accessing a subcarrier at a specific time. This limits the amount of users which connect and use the network at a given time.
On the opposite hand, WiFi 6 uses OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access). It multiplexes the existing subcarrier areas on constant bands. By doing this, users don’t have to wait for a free subcarrier. OFDMA assigns different resource units to multiple users.
This ends up in lesser congestion and delays even multiple devices are connected. OFDMA will increase efficiency and reduces latency.
• Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Outputs (MU-MIMO)
MU-MIMO means that “multi-user, multiple-input, multiple outputs.” It’s a wireless technology that enables over one user to communicate with a router. There’s a huge distinction capability from WiFi 5 to WiFi 6.
WiFi 5 uses a downlink, which means that multiple users are limited to access the router. Once this limit is exceeded, the WiFi 5 becomes thronged and engorged like latency, packet loss, and so on. In WiFi 6, they handle up to eight devices and using the connection with none interference.
The WiFi 6 MU MIMO upgrade is bidirectional, means the computer can hook up with the router on multiple bands. This suggests improved ability to transfer data.
• Frequency Bands
One clear distinction between WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 is the frequency bands. WiFi 5 uses the 5GHz band, that offers less interference. The drawback is the signals are shorter with diminished ability to penetrate the walls and other obstacles.
WiFi 6 uses 2 band frequencies, the 2.4Ghz and the 5Ghz. The fact that WiFi 6 uses each the 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz implies that devices will scan and utilize the band with less interference. That’s way, user gets the most effective networks, quicker speed with comprehensive range.
• BSS Coloring
BSS coloring is another feature of WiFi 6, which is a completely new feature. BSS or basic service sets is a feature that only WiFi 6 and future generations will decipher the BSS coloring using BSS color identifier. This feature is crucial to prevent overlapping signals.
• Latency
Latency refers to the delay in transferring information. Low latency speeds indicate very little or no delay. WiFi 6 offers lesser latency, creating it excellent for businesses and organizations. Users will appreciate this feature because it means quicker internet.
#WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6 – WiFi 6 Is The Next Generation
In 2021, WiFi 6 was launched. WiFi 6 means the technology is extended to incorporate the 6GHz band. It opens full potentialities for the web user compared to WiFi 5. The most essential distinction between these 2 technologies is the gap from a new band frequency.
The 6 GHz band exists without interference or overlap, which suggests less latency and quicker speed! Because the world is moving towards newer technologies like VR and 8k streaming, WiFi 6 is the excellent boost up to the future.
The new WiFi 6 has more channels, which is often a so much from WiFi 5, about 160 megacycle per second on the 5GHz band. One minor downside is that whereas the WiFi 6 bands are backward compatible, though it’s never be a problem for WiFi 5 Vs WiFi 6.
Source:
 Troubleshooting Wifi Solutions connect to the WiFi network
Troubleshooting Wifi Solutions connect to the WiFi network